Podiatric Medicine: Expertise in Foot and Ankle Care
Doctors of podiatric medicine are podiatric physicians and surgeons, qualified by their education, training, and experience to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the foot, ankle, and related structures of the leg.
- Podiatric medicine is a medical sub-specialty, focused on a specific part of the anatomy similar to other highly focused sub-specialties, such as ophthalmology, cardiology, and otolaryngology.
- Within the field of podiatric medicine and surgery, podiatrists can focus on specialty areas such as surgery, sports medicine, biomechanics, geriatrics, pediatrics, orthopedics, or primary care.
Doctors of podiatric medicine have the education, training, experience, and licensure to:
- perform comprehensive medical history and physical examinations;
- prescribe drugs and order and perform physical therapy;
- perform surgeries ranging from basic to complex reconstructive surgery;
- repair fractures and treat sports–related injuries;
- prescribe and fit orthotics, durable medical goods, and custom–made shoes; and
- perform and interpret X–rays and other imaging studies.
Podiatric Medical Education
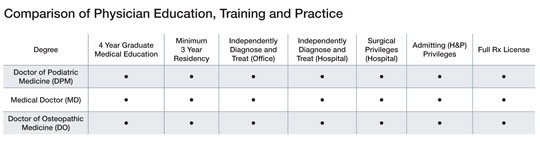
Doctors of podiatric medicine receive basic and clinical science education and training comparable to that of medical doctors:
- Four years of undergraduate education focusing on life sciences
- Four years of graduate study in one of the nine podiatric medical colleges
- At least three years of postgraduate, hospital–based residency training
The education, training, and experience podiatrists receive in the care and treatment of the lower extremity is more sophisticated and specialized than that of broadly trained medical specialists.
Download this issue/policy brief: Podiatric Medicine Expertise in Foot and Ankle Care (PDF)